
At the Hand Therapy Group, we have the skills and experience to assess and treat conditions affecting the hand, wrist and upper limb. Our practice employs physiotherapists and occupational therapists who have undertaken special training to become hand therapists. The majority are Accredited Hand Therapists (as awarded by the AHTA).
We work closely with a number of leading hand surgeons in the Sydney region.
Hand therapy will include a thorough assessment of your problem, advice on how you can manage it, and a home program of exercises and postural correction. We also offer the fabrication of thermoplastic splints and waterproof casts, if required for appropriate fracture care and post-op management.
Trigger Finger
What causes trigger finger?
A small nodule at the flexor tendon sheath contributes to clicking and locking of the fingers when making a fist
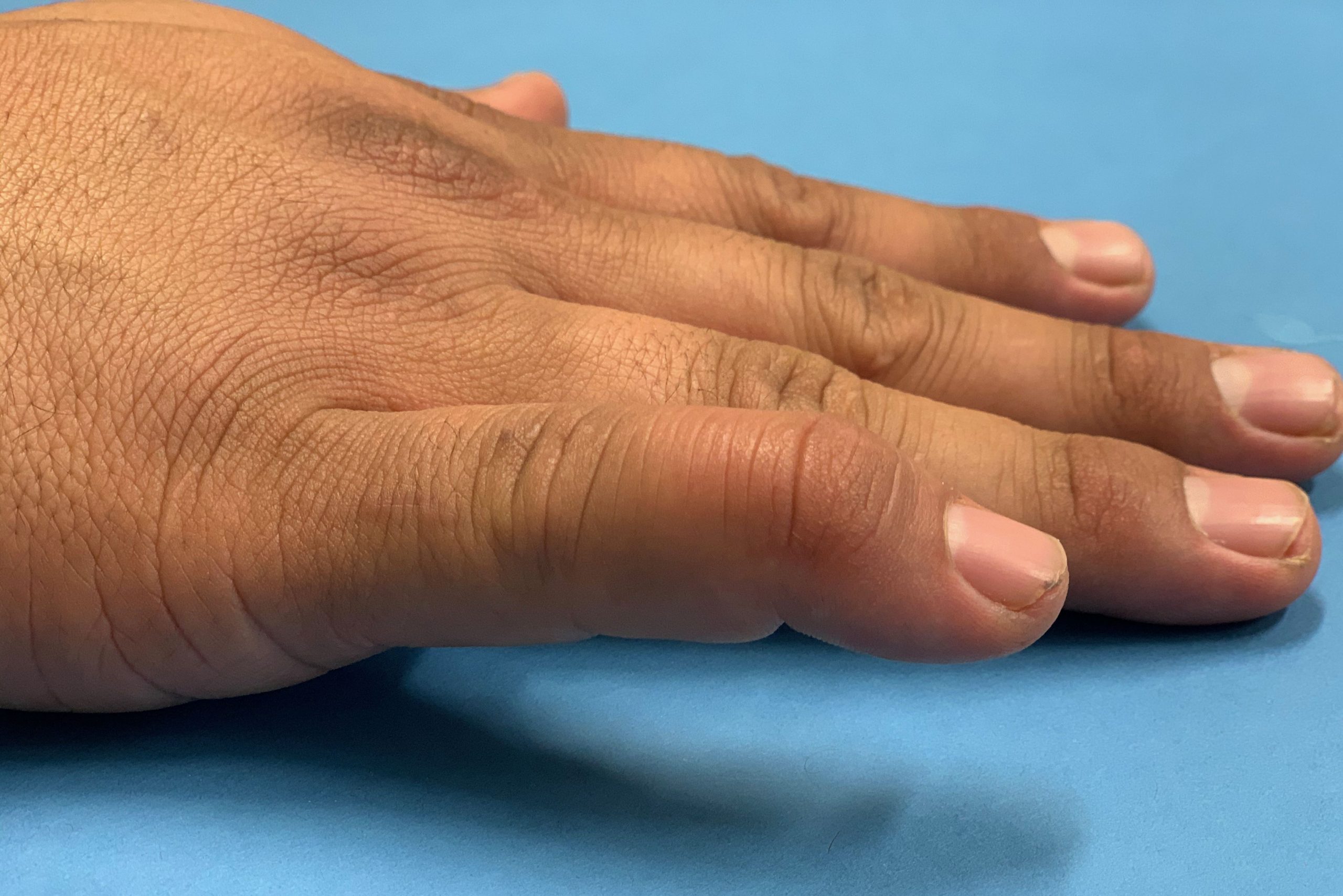
Mallet Finger
What causes mallet finger?
Mallet finger results from either a fracture or rupture of the extensor tendon, resulting in the inability to straighten the tip of your finger. It usually occurs when the tip of the finger is forced to bend, and occurs with ball sports, as well as incidental activities.
Ulnar Sided Wrist Pain
What causes a Triangular Fibrocartilage Complex (TFCC) injury, or ulnar sided wrist pain?
The triangular fibrocartilage complex (TFCC) consists of the triangular fibrocartilage disc, radioulnar ligaments and ulnocarpal ligaments. It stabilises the ulnar side of the wrist and distal radioulnar joint, and absorbs shock from any forces going through your wrist.
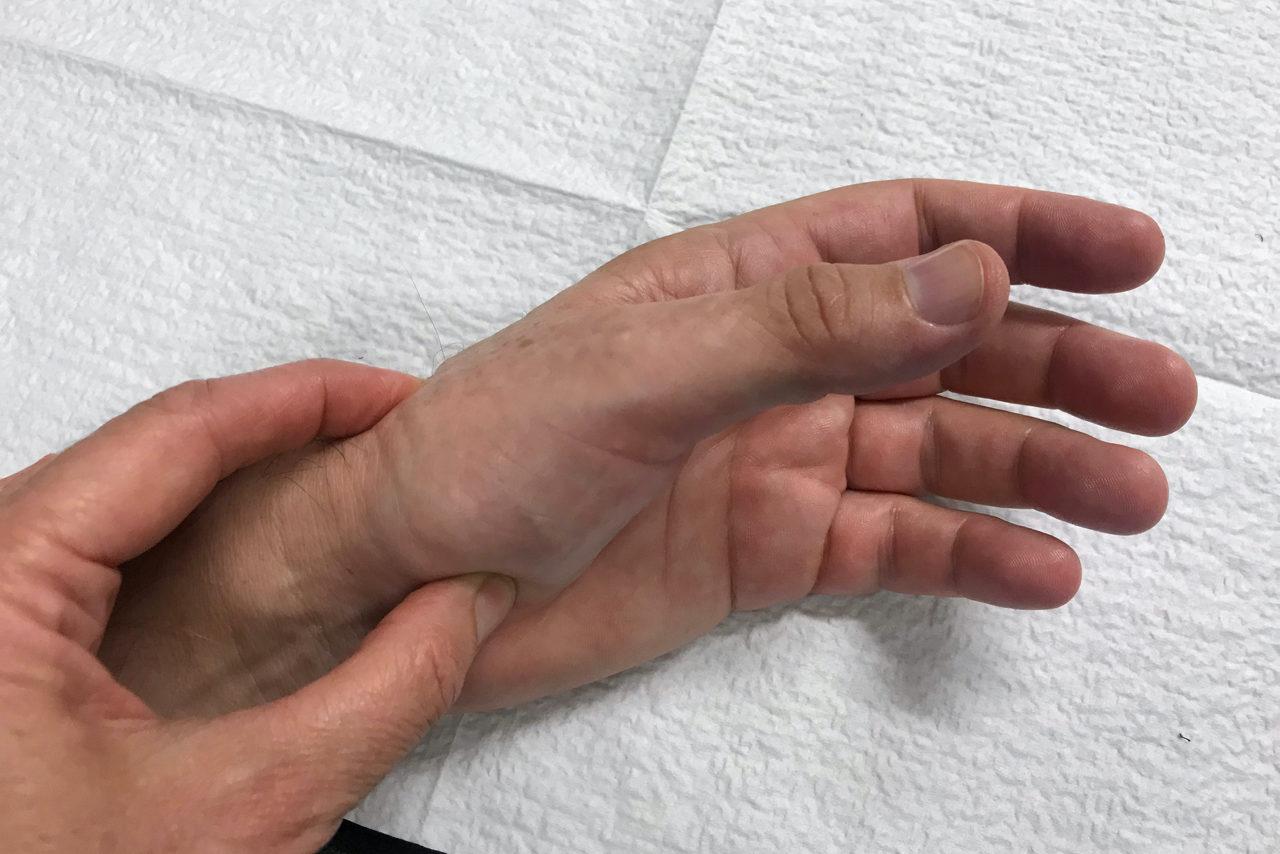
Arthritis at the base of the thumb
Arthritis at the base of the thumb can be painful, impairing your ability to work, perform household tasks, hobbies and sports. We can help you overcome your pain by explaining factors that contribute to your symptoms and creating a treatment plan that addresses current symptoms and reduces the likelihood of flare-ups in the future.
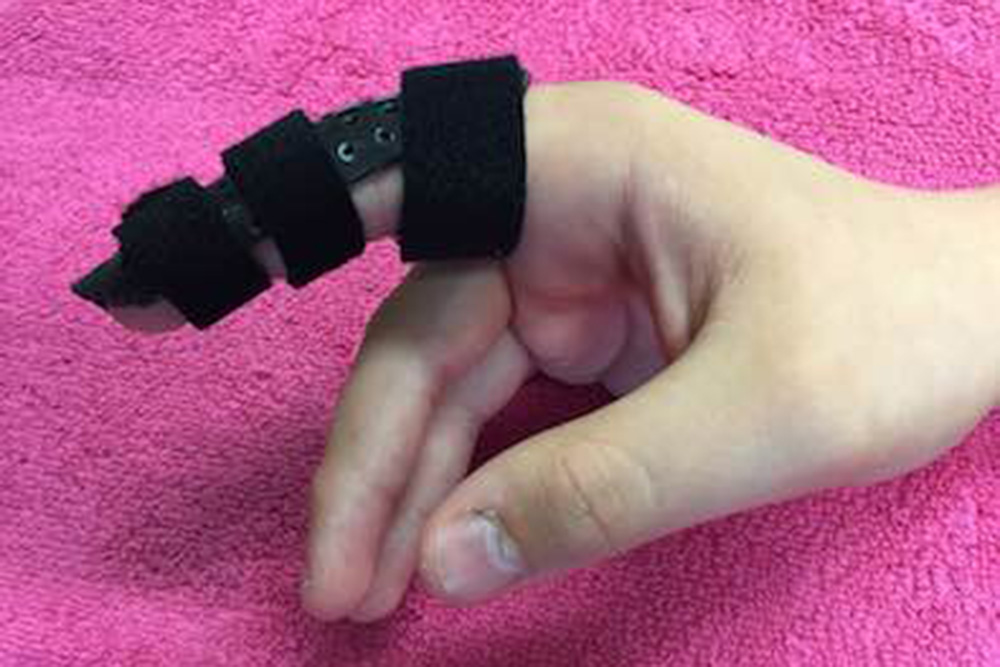
Volar Plate Injury
What causes a volar plate injury?
The volar plate is a ligament which sits at the front of the middle joint. Volar plate injuries occur when the finger is hyperextended eg. catching a ball. The ligament can pull off by itself or with a piece of bone called and avulsion fracture.
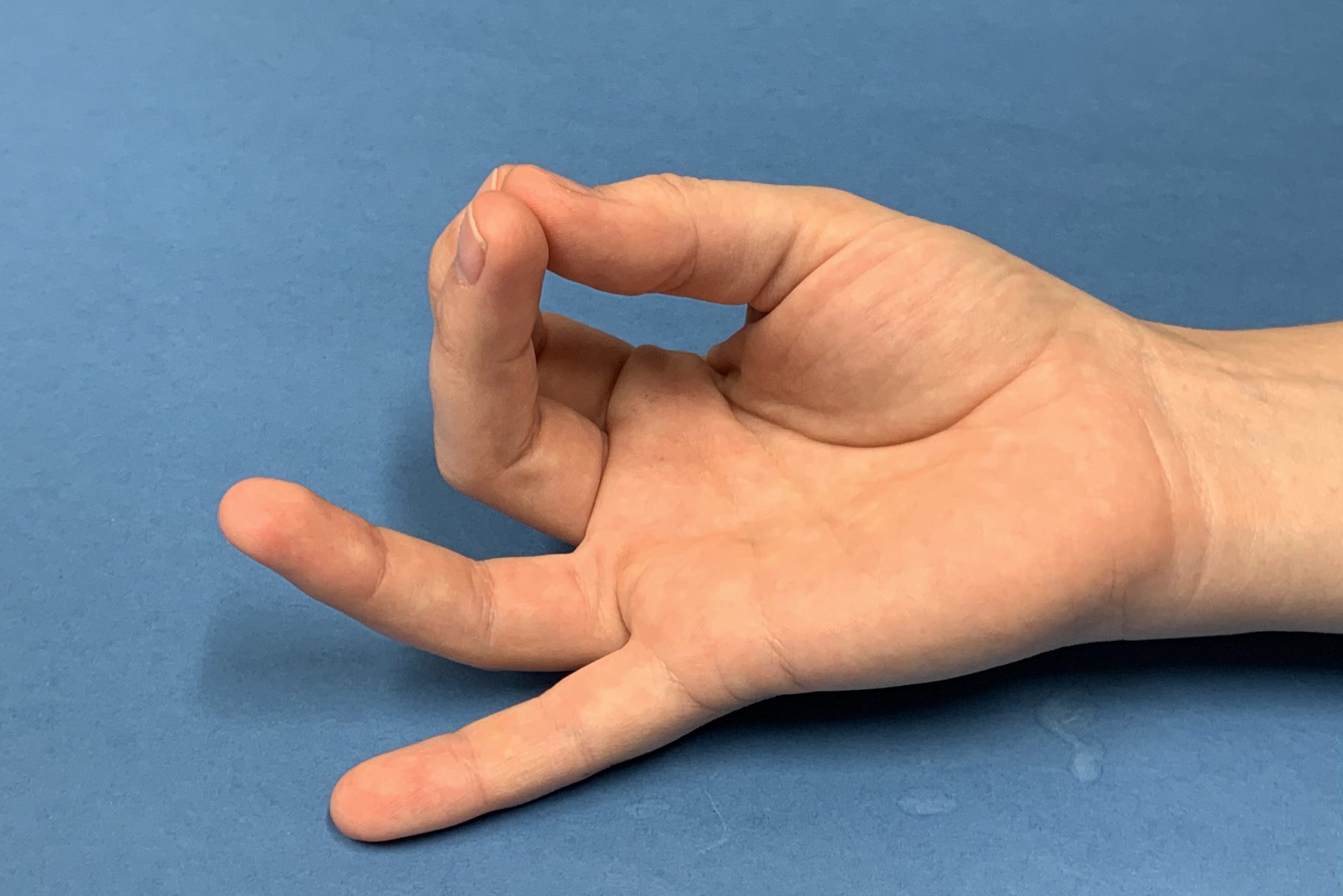
Carpal Tunnel Syndrome
What causes carpal tunnel syndrome?
Carpal Tunnel Syndrome is caused by compression of the median nerve as it passes through the wrist. This may be caused by sustained wrist flexion or gross gripping, vibration, or direct pressure over the carpal tunnel. Increased swelling in the carpal tunnel can also contribute to compression of the median nerve, and may be a factor in late stage pregnancy.

Scapholunate ligament injury
The wrist consists of 8 carpal bones, 2 of them being the scaphoid and the lunate. The scapholunate ligament holds the scaphoid and lunate bone together. This helps to maintain stability of the wrist when gripping or pushing from the wrist.
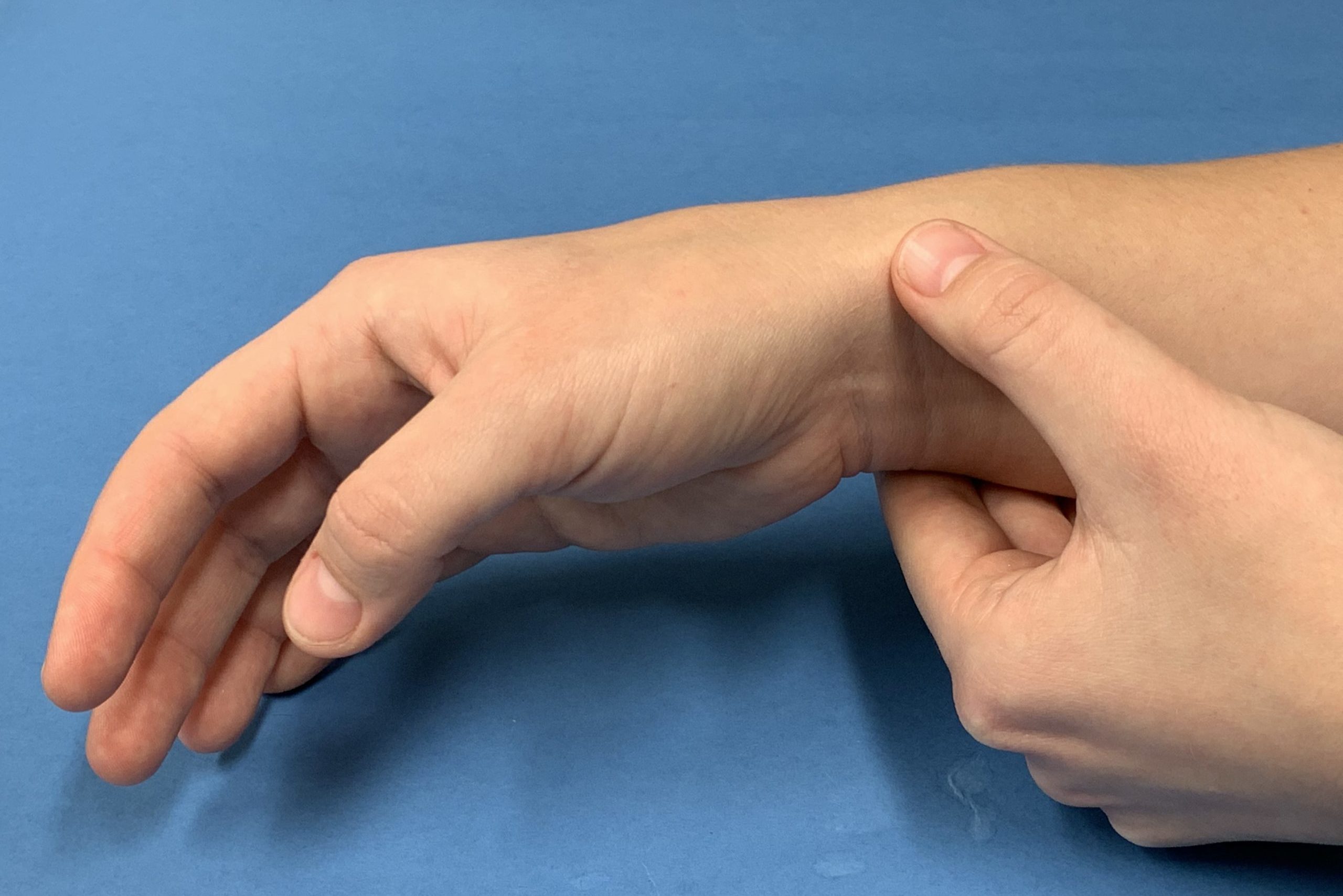
DeQuervain’s Disease
What causes DeQuervain's disease?
De Quervains disease is caused by narrowing of the tendon sheath around two tendons that control the thumb. It is caused by repetitive activities, sustained positioning and occasionally by impact. It is most common in new mothers and middle aged women performing unaccustomed activities.

Hypersensitive scars
Hypersensitive scars can be painful and limit normal functional use of the hand. They can result in the need to posture awkwardly to avoid touch.

Central Slip Injury
What causes a central slip injury?
Central slip injury is often caused by a joint dislocation or forced flexion of the proximal interphalageal joint (PIP joint). This causes rupture of the central slip, which is part of the extensor tendon that straightens the PIP joint. The tendon can tear away from the bone or pull a small fracture fragment with it.
What are the symptoms?
Loss of extension of the middle joint of the finger. If left untreated a boutonniere deformity can occur, where the PIP joint rests in a flexed position and the distal interphalangeal joint (DIP joint) sits in hyperextension. Without the central slip to straighten the PIP joint, other parts of the extensor mechanism collapse creating a deforming force on the finger joints.
How is a central slip injury treated?
Education, splinting, skin care and exercises are required for a period of 6-8 weeks. If the tendon was cut with a sharp object, surgery may be required. After surgery, hand therapy includes wound care, splinting, scar massage, oedema management and active range of movement exercises according to tendon repair protocol.
Your Hand Therapist can show you how to safely don and doff the splint for hygiene whilst maintaining the integrity of the healing central slip tendon. DIP joint flexion exercises are important to maintain the natural balance of the mechanism and prevent a boutonniere deformity.
If you have any questions about a central slip injury, or about another injury to the fingers, hands, wrist, and arms and would like to book an appointment, get in touch today.
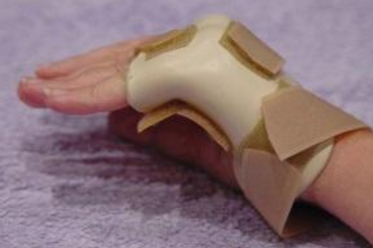
Metacarpal fracture
Metacarpal fractures involve a fracture to the metacarpal bone, which is the long bone in the hand between the wrist and fingers. Metacarpal fractures may be simple or complex. Simple fractures can be managed by splinting or casting, whereas more complex fractures require surgery.
What causes metacarpal fractures?
Metacarpal fractures can be caused by a fall on an outstretched hand, a heavy object falling onto the hand or axial load such as a punch movement.
What are common types of metacarpal fractures?
The most common type of metacarpal fracture is fracture of the 5th metacarpal head, or also known as a Boxer’s fracture. It accounts for 40% of all hand fractures. Boxer’s fracture is commonly caused by an axial pressure applied with a clenched fist such as punching.
Another common metacarpal fracture is fracture to the base of the first metacarpal bone, located at the base of the thumb. This is commonly known as a Bennett’s fracture. They can be an unstable fracture and can dislocate at the CMC joint. This is due to the pull of the muscles and the ligament.
What are the symptoms?
Pain in the hand, especially near the big knuckles on the back of the handSwellingLoss of movement in the finger or knuckleLoss of movement in the angulation of the finger when trying to close a fist
How are metacarpal fractures treated?
Metacarpal fractures require immobilisation in a thermoplastic splint, which is custom made by one of our therapists. Treatment also includes tendon gliding exercises, oedema management and strengthening when fracture has healed.
If the fracture has been fixed via surgery, you will need to see a hand therapist within a few days to commence range of movement exercises, have a custom-made splint fabricated and for wound care.
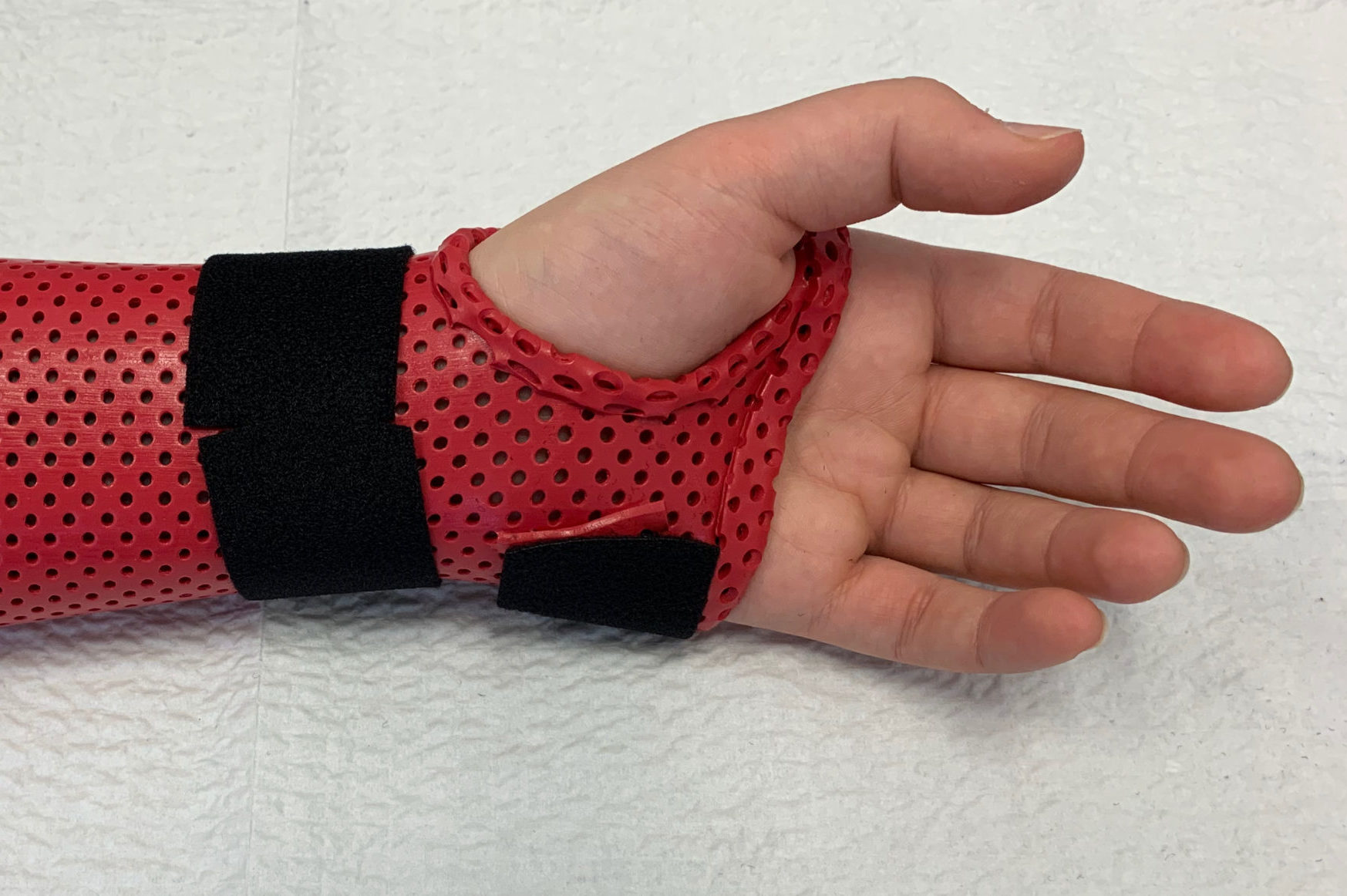
Wrist Fracture
Wrist fractures may be simple of complex. Simple fractures can be managed by casting for six weeks, whereas more complex fractures usually require surgical fixation.
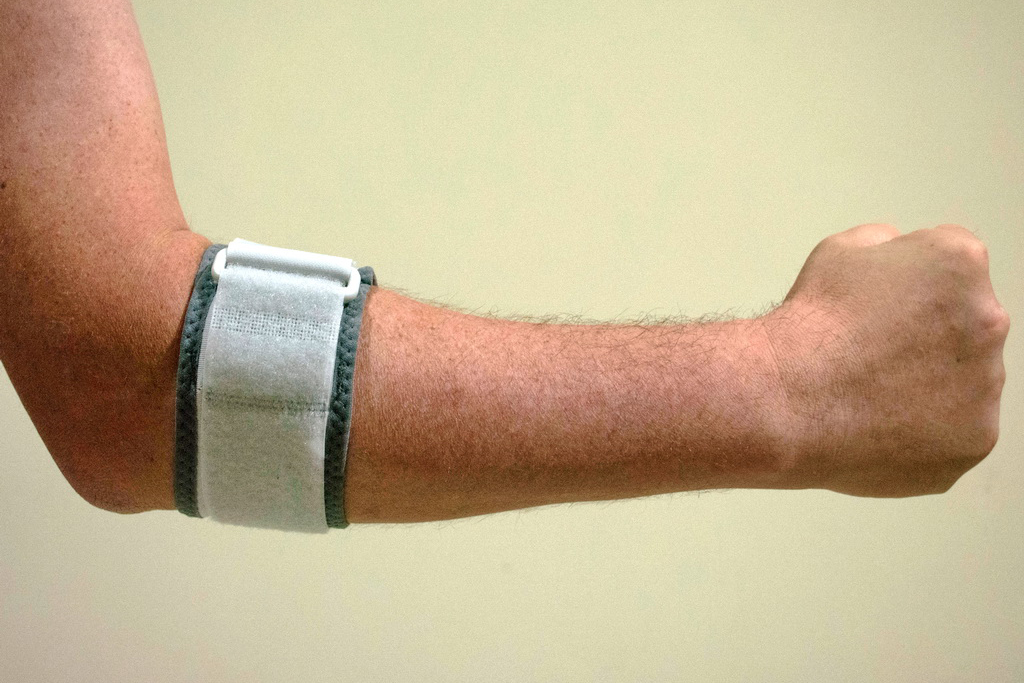
Elbow tendinopathy (tennis elbow)
Elbow tendinopathy – commonly known as tennis elbow – is an injury to the muscles that extend from the elbow to the wrist. Pain can start from different places down the arm (and sometimes even in the neck), generally in the lateral epicondyle, which is the bony outer part of the elbow where muscles from the hand and wrist are attached.
What are common causes of elbow tendinopathy?
Elbow tendinopathy is caused by repetitive use of the muscles that control the wrist, hand and fingers which extend up the forearm, resulting in small tears in the tendon.
Common causes include:
Excessive gripping activities Incorrect hand use while hammering, painting, typing etc Poor muscle and tissue health which makes it more susceptible to injury Incorrect technique while throwing, or hitting (hence its namesake). Tennis players believe the condition comes from high repetition of movement, such as serving, which causes tiny tears to open up in the tissue.
What are the symptoms?
Symptoms of elbow tendinopathy generally appear quite slowly, beginning with pain and a dull ache in the lateral epicondyle after excessive activity. Pain may improve once you have rested. As the condition gets worse, pain can spread down the arm and the elbow will be tender when touched. Pain may be worse after sleeping.
In more severe cases, even the most minimal movements such a turning a key or picking up a plate will be painful. Pain may also be present in the neck.
How is tennis elbow treated?
In most cases, elbow tendinopathy can be treated by wearing an elbow and or wrist brace, stopping any activities that worsens pain, nerve gliding exercises, joint mobilisations and graded strengthening.
Surgery may be required if symptoms don’t improve with wearing a brace, exercises and or cortisone injection. Your therapist can discuss with you and your GP and arrange a referral to a surgeon if required.
If you are suffering from any of these symptoms, or any other issues with the hand, arm or fingers, please feel free to get in touch, we’d be more than happy to help.
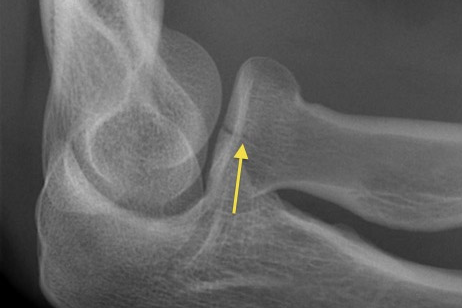
Elbow fracture
The elbow is made up of three main bones: the humerus, the radius and the ulna. The elbow joint consists of portions of these three bones: the distal humerus, the radial head and the olecranon. An elbow fracture is a break to any of these portions of the arm.
The three main types if elbow fractures include radial head or neck fractures, olecranon fractures and distal humerus fractures.
What are common causes of an elbow fracture?
Elbow fractures are often caused by fall on out stretched hand
What are the symptoms?
A broken elbow will be extremely debilitating due to the complexity of the region. Pain, numbness and weakness throughout the entire arm is common, and the elbow joint will be extremely painful, bruised and swollen making it hard to move. A snap or pop may be audible when impact occurs.
How are elbow fractures treated?
Some elbow fractures where the joint is not dislocated can be treated in a cast or thermoplastic splint. Surgery is usually required for severe breaks with displaced fractures. Fixation devices including screws, plates, nails or K-wire will help stabilise the healing process. You will usually be referred to a Hand Therapist following surgery to help control swelling, regain motion, and provide a removable brace to protect the surgical site.
If you have any questions regarding a broken arm or elbow, please don’t hesitate to get in touch with us today for an appointment.

Finger Sprains and Dislocations
Finger sprains and dislocations most commonly occur at the proximal interphalangeal joint (PIPJ). When a finger is sprained, it is likely that the collateral ligaments or volar plate that surrounds PIPJ has been torn. PIPJ dislocations may occur if the finger sprain is severe. Finger sprains and dislocations often occurs when the finger is hyperextended. This happens regularly during ball sports when the ball hits the end of the finger.
Dupuytren's Contracture
Dupuytren's Contracture results in the inability to straighten fingers.

Flexor Tendon Injury
Flexor tendons are cords that connect muscles to bone. The flexor tendons run from the elbow and attach onto the palm of your fingers and thumb. They help to bend the finger and thumb in daily activities such as holding onto a bag, buttoning shirts and writing.
What are common causes of Flexor Tendon Injury?
Flexor Tendons are most commonly injured via a traumatic accident, such as cutting with a knife, blender or power tools. Injuries can also occur from sport when the finger is caught on someone’s clothes, namely a “Jersey Finger.”
What are the symptoms?
Unable to bend the tips of your fingers or thumbBleeding, pain and swelling (if the hand was cut with a sharp object)
What treatment is there for a Flexor Tendon Injury?
Surgery is required for the treatment of a Flexor Tendon Injury to reattach the tendons. Your Hand Surgeon will notify you when you are required to attend hand therapy, usually within 2-3 days after surgery date.
Hand therapy treatment will include wound management, fabrication of protective forearm splint, swelling management and range of movement exercises if appropriate. Hand therapy is crucial for rehabilitation after surgery to ensure your hand has the best outcome.
